TDD实践——从零写一个简单的Mybatis——TinyBatis
大约 4 分钟
前言
之前有幸学习过徐昊的 TDD 课程,收获颇大,但是一直没有好的 idea 去实践,这次就用 TDD 的模式来实现一个简单的 Mybatis,取名为 TinyBatis。
TDD 流程
以下仅为个人理解,一千个读者就有一千个哈姆雷特,欢迎大家探讨。
TDD(Test-Driven Development)核心是一套指导思想。
之前笔者编程的模式一直是:先写代码,后写测试。
这样编程会带来几个很麻烦的问题:
- 代码写完后,测试用例写起来很麻烦,因为代码的设计并没有考虑到测试用例,所以测试用例写起来很费劲。
- 严重依赖模块、代码结构设计,写起来很容易卡壳。
- 误导排期和进度,代码写完了不代表功能完成了。
而 TDD 的核心思想是:先写测试,后写代码:
- 编写测试用例,测试用例是对功能的需求的描述,有助于理解需求(需求都没理解,怎么可能写好代码);
- 测试用例反推代码结构,有利于写出测试良好的代码;
- 重构方便,完备的测试用例保证了重构后代码的正确性;
有了 TDD 思想指导后,笔者的流程是这样的:
- 理解需求,先写入口测试用例;
- 从入口测试用例反推代码结构,写出测试良好的代码;
- 通过测试用例;
- 发现不合理代码,重构再通过测试用例;
需求
TinyBatis 的需求是这样的:
支持从XML配置构建SqlSessionFactory,SqlSessionFactory可以创建SqlSession,SqlSession可以执行Mapper中的select语句。
TDD 真的不好用文字描述,本文写的稀烂,勉强能看,权当做个人 TDD 笔记吧。 代码直接参考这里。
测试用例
这样的一句话需求肯定是让人难受的(PM 经常这样干)。
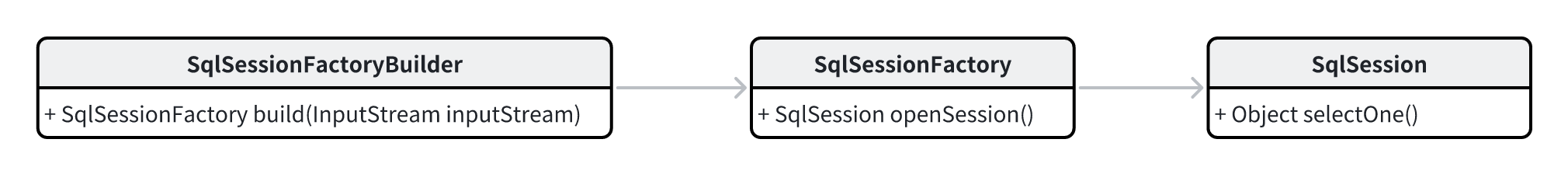
拆解一下需求,将其转化为测试用例:
@Test
public void testWithXml1() throws Exception {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = ResourceUtil.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
}
- 读取
mybatis-config.xml配置文件;
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="org.h2.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:h2:mem:demo;INIT=runscript from 'classpath:create.sql'"/>
<property name="username" value="sa"/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="BlogMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 新建
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder解析配置文件,构建SqlSessionFactory;
下面让这个测试用例通过:
新建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类,新建build方法:
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return new SqlSessionFactory(configurationConfig);
}
}
新建SqlSessionFactory类:
public class SqlSessionFactory {
public SqlSessionFactory() {
}
public SqlSession openSession() {
return new SqlSession();
}
}
最后新建SqlSession类:
public class SqlSession implements AutoCloseable {
public SqlSession() {
}
}
运行测试,测试通过。
渐进式开发
读取 XML 配置文件
第一个测试用例通过了,接下来就是实现第一个小需求:读取mybatis-config.xml配置文件。
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
ConfigParser configParser = new ConfigParser();
try {
ConfigurationConfig configurationConfig = configParser.parse(inputStream);
return new SqlSessionFactory(configurationConfig);
} catch (DocumentException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("parse mybatis-config.xml error", e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("load driver error", e);
}
}
}
新建ConfigParser类,实现parse方法:
public class ConfigParser {
public ConfigurationConfig parse(InputStream is) throws DocumentException {
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
Document document = saxReader.read(is);
Element configurationElement = document.getRootElement();
if (!configurationElement.getName().equals("configuration")) {
throw new RuntimeException("root should be <configuration>");
}
Element environmentsElement = configurationElement.element("environments");
String defaultEnvironment = environmentsElement.attribute("default").getValue();
List<EnvironmentConfig> environmentConfigs = parseEnvironments(environmentsElement);
Element mappersElement = configurationElement.element("mappers");
List<MapperConfig> mapperConfigs = parseMappers(mappersElement);
List<MapperNode> mapperNodes = new ArrayList<>(mapperConfigs.size());
// Parse Mapper XML files
MapperParser mapperParser = new MapperParser();
for (MapperConfig mapperConfig : mapperConfigs) {
InputStream mapperConfigInputStream = ResourceUtil.getResourceAsStream(mapperConfig.getResource());
MapperNode mapperNode = mapperParser.parse(mapperConfigInputStream);
mapperNodes.add(mapperNode);
}
return new ConfigurationConfig(defaultEnvironment, environmentConfigs, mapperConfigs, mapperNodes);
}
// ...
}
读取 Mapper XML 文件
public class MapperParser {
public MapperNode parse(InputStream is) throws DocumentException {
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
Document document = saxReader.read(is);
Element mapperElement = document.getRootElement();
if (!mapperElement.getName().equals("mapper")) {
throw new RuntimeException("root should be <mapper>");
}
// ...
return new MapperNode(namespace, selectNodes);
}
}
支持if语句
<select id="selectOne" resultType="github.io.pedrogao.tinybatis.Blog">
select * from blog where id = ?
<if test="title != null">
and title = ?
</if>
</select>
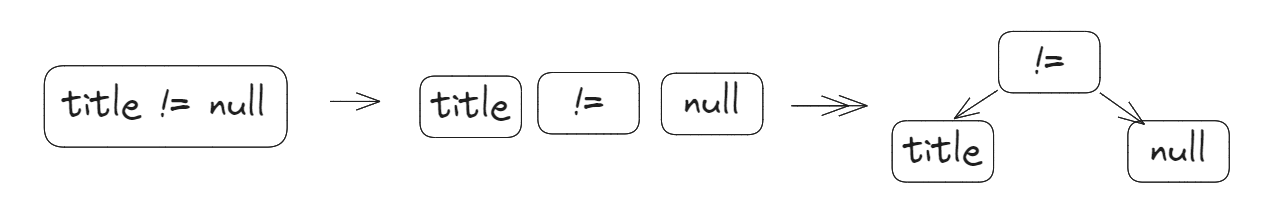
IfNode类中解析test语句,并得到 tokens:
public class IfNode {
private String test;
private String subSql;
private List<Token> tokens;
public IfNode(String test, String subSql) {
this.test = test;
this.subSql = subSql;
this.tokens = new Lexer(test, Rule.DEFAULT_RULES).tokenize();
}
// ...
}
解析完成后在SqlSession中解释执行:
public Object selectOne(String id, Map<String, Object> variables, Object... params) {
try {
SelectNode selectNode = selectNodeMap.get(id);
if (selectNode == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("selectNode not found");
}
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder(selectNode.getSql());
for (var ifNode : selectNode.getIfNodes()) {
String subSql = ifNode.getSubSql();
Parser parser = new Parser(ifNode.getTokens());
Expr expr = parser.parseExpr(); // 1. 解析得到表达式
Object res = interpreter.interpret(expr, variables); // 2. 执行表达式
if (res != null && (Boolean) res) { // 3. 如果结果为 true,拼接 subSql
sql.append(" ").append(subSql);
}
}
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql.toString());
}
}
